How To Choose Cleaning Agents For Heat Exchangers?
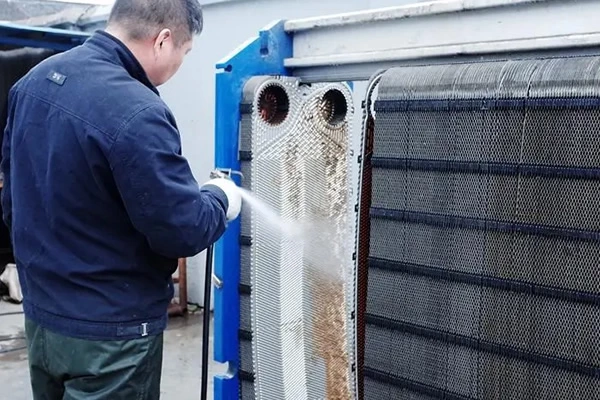
When cleaning heat exchangers, the first step is to determine the cleaning area and the plate material of the heat exchanger. After sampling and analysis, reagents are selected based on the material and degree of scaling of the heat exchanger. For carbon steel materials mainly composed of carbonate scale and rust, hydrochloric acid is generally chosen as the main acid washing solution for better results. For safety reasons, organic acid amino sulfonic acid can also be chosen as the main acid washing solution;
For stainless steel, nitric acid is generally chosen as the best cleaning acid, and for safety reasons, mild acidic amino sulfonic acid can also be selected as the main cleaning acid according to the actual situation.
In some special cases, it mainly refers to the possibility of defects, thinness or other special circumstances in the cleaning material, which should be carefully considered.
For example, when cleaning copper material heat exchangers, it is important to pay attention to which copper material is used. Special attention should be paid to brass, which is mainly composed of copper and has a relatively high content of zinc. In order to prevent the occurrence of zinc removal, the concentration of the pickling solution should be selected as low as possible. Generally, corrosion inhibitors have poor effects on protecting both copper and zinc metals. Therefore, a gentle cleaning method should be adopted during the operation, that is, low concentration, short time, low flow rate, and room temperature cleaning is better. Generally, Lan-826 is the preferred corrosion inhibitor. For other additives such as surfactants, clay stripping agents, foaming agents, etc., they can be selected based on the principles of cleaning agent selection and specific circumstances.
Welcome To Visit Our Official Website!
If you have any questions, please contact us through the following ways, we will give you the most sincere service!