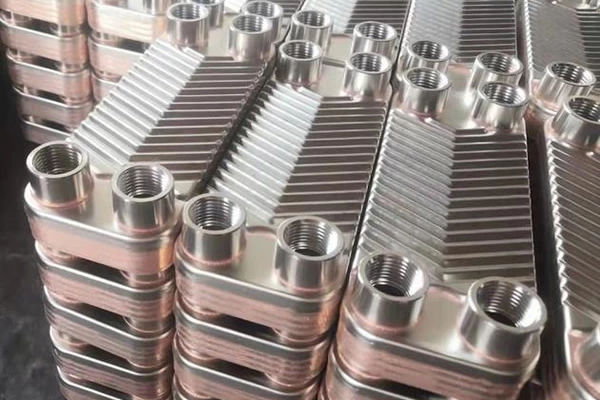
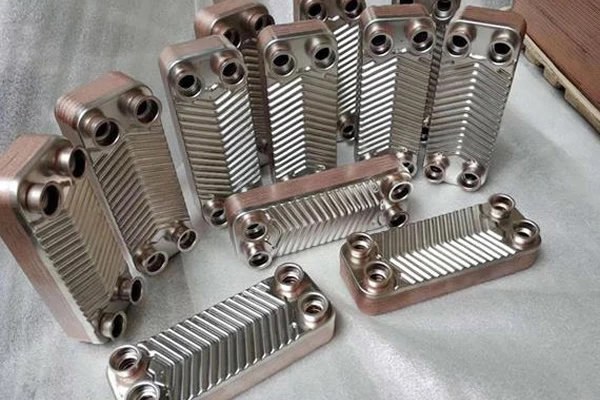
What are the differences between horizontal and vertical corrugations of PHE plates in practical applications?
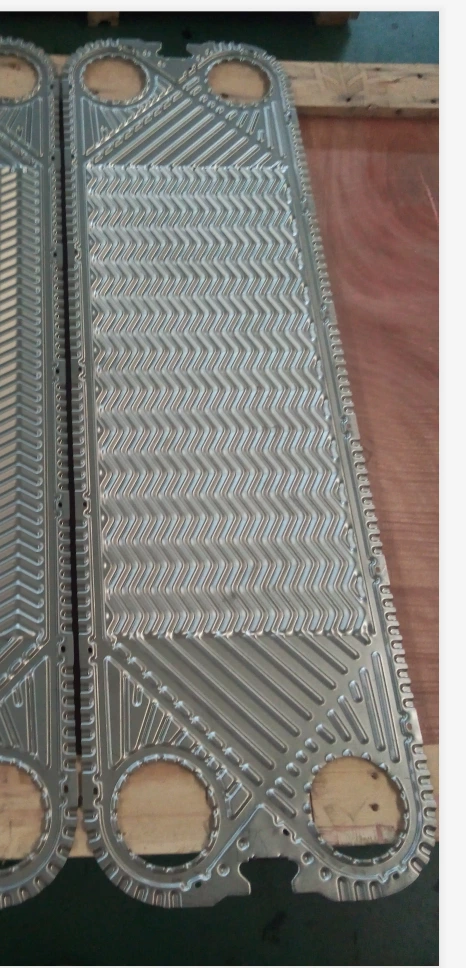
Horizontal corrugated plate:
The ripple direction of the transverse wave pattern plate is perpendicular to the fluid flow direction, which helps to increase the surface area of the plate and improve heat exchange efficiency.
The design of horizontal plates can enhance heat exchange efficiency, enabling them to handle larger heat loads at the same size.
In addition, this design can also adapt to high temperature and high pressure working environments, as the structure of corrugated sheets is more robust and can withstand higher pressures.
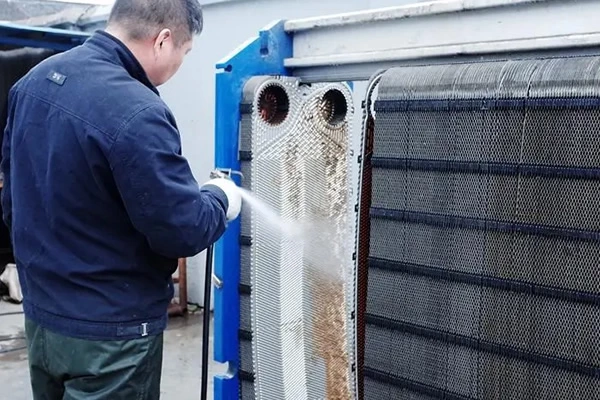
However, the cleaning and maintenance of transverse corrugated plates are relatively complex and require more time and effort.

Vertical corrugated plate:
The corrugated direction of the vertical corrugated plate is parallel to the fluid flow direction, which can also enhance heat transfer, increase the strength and rigidity of the plate, and thus improve the pressure bearing capacity of the plate heat exchanger.
The design of vertical corrugated plates can also promote fluid turbulence, which helps to reduce the formation of sediment or dirt and has a certain "self-cleaning" effect.
Compared with horizontal corrugated plates, vertical plates may be more economical and convenient in terms of manufacturing cost, cleaning, and maintenance.
Overall, both horizontal and vertical corrugated plates have their own advantages.
The choice of plate type depends on specific application requirements, including heat exchange efficiency, fluid properties, working pressure, cost, and ease of maintenance.

Welcome To Visit Our Official Website!
If you have any questions, please contact us through the following ways, we will give you the most sincere service!